Introduction to Blood Sugar Diabetes
In today’s fast-paced world, where unhealthy lifestyle choices are becoming increasingly common, the prevalence of blood sugar diabetes is on the rise. Understanding this condition is crucial for effective management and prevention. Let’s delve into the intricacies of blood sugar diabetes, its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and much more.
Understanding Blood Sugar and Insulin

Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is a vital source of energy for the body’s cells. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the absorption of glucose into cells. However, in diabetes, this process is disrupted, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Types of Diabetes

Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to survive.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, typically occurring in adults. It develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Lifestyle factors such as obesity, unhealthy diet, and physical inactivity play a significant role in its development.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes interfere with insulin function. Although it usually resolves after childbirth, women with gestational diabetes have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes and Risk Factors
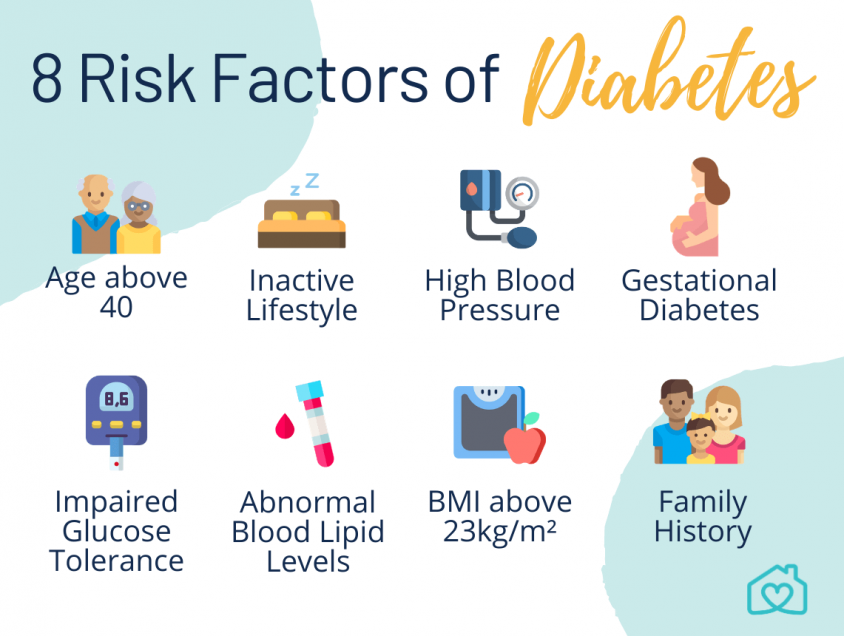
While the exact cause of diabetes remains unclear, several factors contribute to its development. Genetics, family history, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and ethnic background can increase the risk of developing diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes
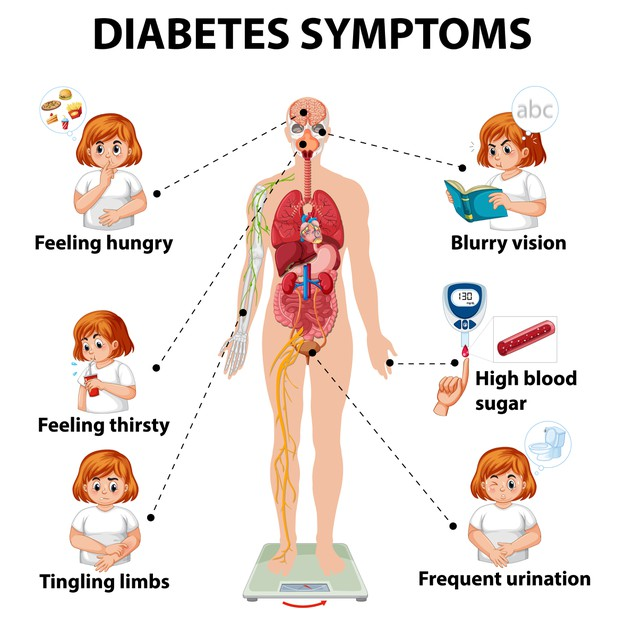
Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and recurrent infections. However, some individuals may remain asymptomatic, especially in the early stages of the disease.
Diagnosis and Monitoring

Diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests that measure fasting blood sugar levels, oral glucose tolerance, and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes effectively and preventing complications.
Treatment Options
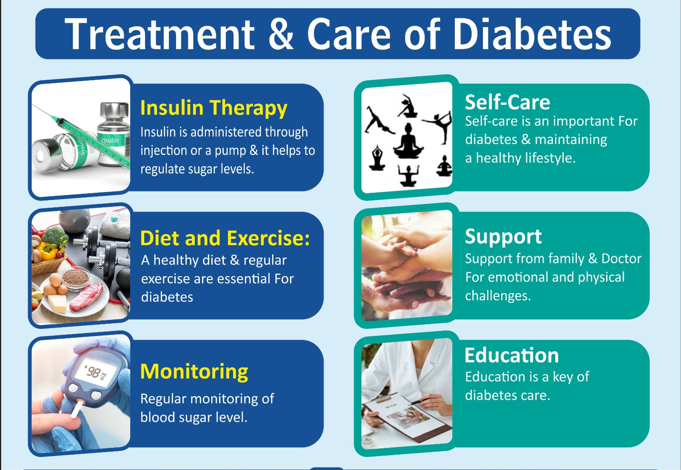
Lifestyle Changes
Making healthy lifestyle choices is the cornerstone of diabetes management. This includes adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, along with regular physical activity and weight management.
Medications
In addition to lifestyle modifications, various medications are available to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. These may include oral antidiabetic drugs, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, and thiazolidinediones.
Insulin Therapy
For individuals with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy is necessary to regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin can be administered through injections or insulin pumps, tailored to individual needs and lifestyle.
Complications of Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications affecting various organs and systems in the body. These include cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage (neuropathy), eye problems (retinopathy), foot complications, and skin conditions.
Prevention and Management Tips
Preventing diabetes involves adopting a healthy lifestyle early on, maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption. For those already diagnosed with diabetes, proper management is essential to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Diet and Nutrition for Diabetes
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in diabetes management, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and maintain overall health. Focus on eating whole foods, controlling portion sizes, monitoring carbohydrate intake, and avoiding sugary beverages and processed foods.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is beneficial for diabetes management, helping to lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, manage weight, reduce stress, and boost overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises.
Importance of Regular Checkups
Regular checkups with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring blood sugar levels, assessing overall health, detecting any complications early on, and adjusting treatment plans accordingly. Stay proactive in managing diabetes and communicate openly with your healthcare team.
Support and Resources for Diabetes Management

Living with diabetes can be challenging, but you’re not alone. Seek support from family, friends, support groups, and healthcare professionals who can provide guidance, encouragement, and practical tips for managing diabetes effectively.
Living with Diabetes: Coping Strategies

Living with diabetes requires resilience, determination, and a positive mindset. Focus on self-care, prioritize your health, stay informed about diabetes management, set realistic goals, celebrate small victories, and don’t hesitate to ask for help when needed. Remember, with the right support and resources, you can thrive despite diabetes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood sugar diabetes is a complex but manageable condition that requires a holistic approach to treatment and prevention. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, making healthy lifestyle choices, adhering to treatment plans, and seeking support when needed, individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives and minimize the risk of complications.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Is diabetes preventable? Yes, type 2 diabetes is largely preventable through lifestyle modifications such as healthy eating, regular exercise, weight management, and avoiding tobacco use.
- Can diabetes be cured completely? While there is no cure for diabetes, proper management can help control blood sugar levels and prevent complications, allowing individuals to lead active and healthy lives.
- What are the long-term complications of diabetes? Long-term complications of diabetes may include heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, nerve damage, eye problems, foot complications, and skin conditions.
- How often should I check my blood sugar levels? The frequency of blood sugar monitoring may vary depending on individual circumstances and treatment plans. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
- What support services are available for individuals with diabetes? There are various support services and resources available, including diabetes education programs, support groups, online forums, counseling services, and healthcare professionals specializing in diabetes care.
Click Below To Know More About Thyroid⬇️
Mastering Thyroid Health: Proven Methods for Control and Prevention


